Are Fish Part Of The Animal Kingdom
The highest category in the traditional Linnaean system of classification is the kingdom . At this level, organisms are distinguished on the basis of cellular arrangement and methods of nutrition. Whether they are single- or multiple-celled and whether they blot, ingest, or produce nutrient are critical factors. Based on these types of distinctions, the biological sciences ascertain at least v kingdoms of living things:
| Kingdom | Types of Organisms | |
| | | |
| Monera | leaner, blueish-green algae (cyanobacteria), and spirochetes | |
| Protista | protozoans and algae of diverse types | |
| Fungi | funguses, molds, mushrooms, yeasts, mildews, and smuts | |
| Plantae | mosses, ferns, woody and not-woody flowering plants | |
| Animalia | sponges, worms, insects, fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals |
Nigh macroscopic creatures are either plants or animals. Of course, humans are animals. The distinction between the found and fauna kingdoms is based primarily on the sources of nutrition and the capability of locomotion or movement. Plants produce new cell thing out of inorganic fabric past photosynthesis. They do not have the ability to move around their environment except by growing or being transported by air current, water, or other external forces.
 |  | |
| Kingdom Animalia | ||
| Kingdom Plantae |
In contrast, animals do not produce their own food but must consume other organisms to obtain it. Animals are generally more than complex structurally. Unlike plants, they accept nerves and muscles that aid in rapid, controlled move around their surround. Animal cells unremarkably do non take rigid walls similar those of plants. This accounts for the fact that your skin and mankind are flexible and the trunk of a tree is not.
This simple dichotomy between plants and animals is not acceptable to encompass all life forms. Some organisms accept characteristics which exercise not qualify them to fit neatly into either kingdom. For instance, funguses and most leaner do not photosynthesize and well-nigh of them lack a ways of controlled locomotion. Some organisms have attributes of both plants and animals. For instance, in that location is a group of common single-cell species living in fresh water ponds called Euglena that photosynthesize and accept their own means of locomotion (whip-similar tail structures called flagella). Because of these and other exceptions, new kingdoms of living things had to be created.
Research done over the final half century has shown us that at that place are fifty-fifty stranger single-celled organisms known as archaeobacteria that live in extremely harsh anaerobic environments such as hot springs, deep sea volcanic vents, sewage treatment plants, and swamp sediments. Different other life forms, they commonly get their energy from geological sources rather than from the sun. There are also microscopic things that are not quite live past definition but have some characteristics that are similar to living things. These are the viruses and prions. It is like shooting fish in a barrel to overlook the importance of these extremely modest things considering they cannot be seen with the naked eye. Notwithstanding, there are very likely around ten times every bit many viruses as all living things put together. There are near l 1000000 viruses in ane cm � of ocean water. It has been estimated that these viruses are responsible for the death of 20% of all oceanic bacteria every day, thereby keeping the phenomenal reproductive capability of bacteria under control. There are also circuitous interactions between bacteria, viruses, and other microbial life forms within our own bodies. Most of the fourth dimension, there are well-nigh 10 times as many microbial cells within us equally there are body cells.
Phylum
Immediately below kingdom is the phylum ![]() level of classification. At this level, animals are grouped together based on similarities in basic body plan or arrangement. For example, species in the phylum Arthropoda
level of classification. At this level, animals are grouped together based on similarities in basic body plan or arrangement. For example, species in the phylum Arthropoda ![]() accept external skeletons likewise as jointed bodies and limbs. Insects, spiders, centipedes, lobsters, and crabs are all arthropodsouthward.
accept external skeletons likewise as jointed bodies and limbs. Insects, spiders, centipedes, lobsters, and crabs are all arthropodsouthward.
In contrast, members of the phylum Mollusca ![]() have soft, unsegmented bodies that are usually, but non always, enclosed in hard shells. They also usually have at least one stiff foot that helps them motility. Octopi, squids, cuttlefish, snails, slugs, clams, and other shellfish are mollusthousand s.
have soft, unsegmented bodies that are usually, but non always, enclosed in hard shells. They also usually have at least one stiff foot that helps them motility. Octopi, squids, cuttlefish, snails, slugs, clams, and other shellfish are mollusthousand s.
 | |
| Bilateral symmetry (phylum Chordata) |
There are at least 33 phyla (plural of phylum) of animals. Humans are members of the phylum Chordata ![]() . All of the chordates take elongated bilaterally symmetrical
. All of the chordates take elongated bilaterally symmetrical ![]() bodies. That is to say, the left and right sides are essentially mirror images of each other. If at that place are 2 functionally similar body parts, they are usually found roughly equidistant from the eye line, parallel to each other. Note the location of the woman's eyes, nostrils, and cheeks relative to the centre line of her trunk.
bodies. That is to say, the left and right sides are essentially mirror images of each other. If at that place are 2 functionally similar body parts, they are usually found roughly equidistant from the eye line, parallel to each other. Note the location of the woman's eyes, nostrils, and cheeks relative to the centre line of her trunk.
 | |
| Gill slits (phylum Chordata) |
At some time in their life cycle, chordates take a pair of lateral gill slits or pouches used to obtain oxygen in a liquid environment. In the case of humans, other mammals, birds, and reptiles, lungs replace rudimentary gill slits later the embryonic stage of development. Frogs replace them with lungs in the transition from tadpoles to adults. Fish retain their gill slits all of their lives.
Chordates also have a notochord ![]() at some phase in their life wheel. This is a rudimentary internal skeleton fabricated of stiff cartilage that runs lengthwise under the dorsal surface of the body. Generally, there is a single hollow nervus chord on top of the notochord. Amongst humans and the other vertebrates, the notochord is replaced by a more than complex skeleton following the embryonic stage of evolution.
at some phase in their life wheel. This is a rudimentary internal skeleton fabricated of stiff cartilage that runs lengthwise under the dorsal surface of the body. Generally, there is a single hollow nervus chord on top of the notochord. Amongst humans and the other vertebrates, the notochord is replaced by a more than complex skeleton following the embryonic stage of evolution.
Members of the phylum Chordata also often have a caput, a tail, and a digestive system with an opening at both ends of the body. In other words, the torso organization is substantially that of a tube in which nutrient enters 1 end and waste affair passes out of the other. The chordates include mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, as well every bit the archaic lancelets (or amphioxus ) and tunicates (or sea squirts).
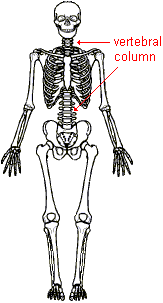 | |
| Human being skeleton |
Subphylum
The chordates are divided into iii subphyla. Humans are members of the subphylum Vertebrata ![]() . Among the vertebrates, the uncomplicated hollow dorsal nerve tube is replaced by a more complex tubular bundle of fretfulness chosen a spinal cord. A segmented vertebral (or spinal) column of cartilage and/or os develops around the spinal string of vertebrates to protect it from injury. At one end of the spinal cord is a head with a brain and paired sense organs that function together to coordinate movement and sensation.
. Among the vertebrates, the uncomplicated hollow dorsal nerve tube is replaced by a more complex tubular bundle of fretfulness chosen a spinal cord. A segmented vertebral (or spinal) column of cartilage and/or os develops around the spinal string of vertebrates to protect it from injury. At one end of the spinal cord is a head with a brain and paired sense organs that function together to coordinate movement and sensation.
Vertebrata is the most avant-garde and numerous subphylum of chordates. It includes all of the fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Collectively, there are virtually 43,000 living vertebrate species in comparison to merely over 1500 species in the other two invertebrate subphyla of chordates.
NOTE: Because scientific discipline is constantly expanding our knowledge of living things, the precise details of how organisms are classified in the Linnaean system are oft in flux. This is not due to defoliation simply rather to the evolution of our understanding brought about by new discoveries. For instance, as a issue of the discovery of a dramatically new grade of life known as archaeobacteria, a growing number of rese archers now apply a classification level above kingdoms referred to as a domain. They ascertain 3 domains of living things: Archaeo (simple leaner-similar organisms that alive in extremely harsh anaerobic environments--these are the archaeobacteria), Bacteria (all other bacteria, blueish-green algae, and spirochetes), and Eukarya (organisms with singled-out nuclei in their cells--protozoans, fungi, plants, and animals).
Copyright � 1998-201three by Dennis O'Neil. All rights reserved.
illustration credits
Source: https://www2.palomar.edu/anthro/animal/animal_3.htm
Posted by: taylorsockle.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Are Fish Part Of The Animal Kingdom"
Post a Comment